F1 Generation Biology Definition
Genetics Den Genetics den Principle of Segregation

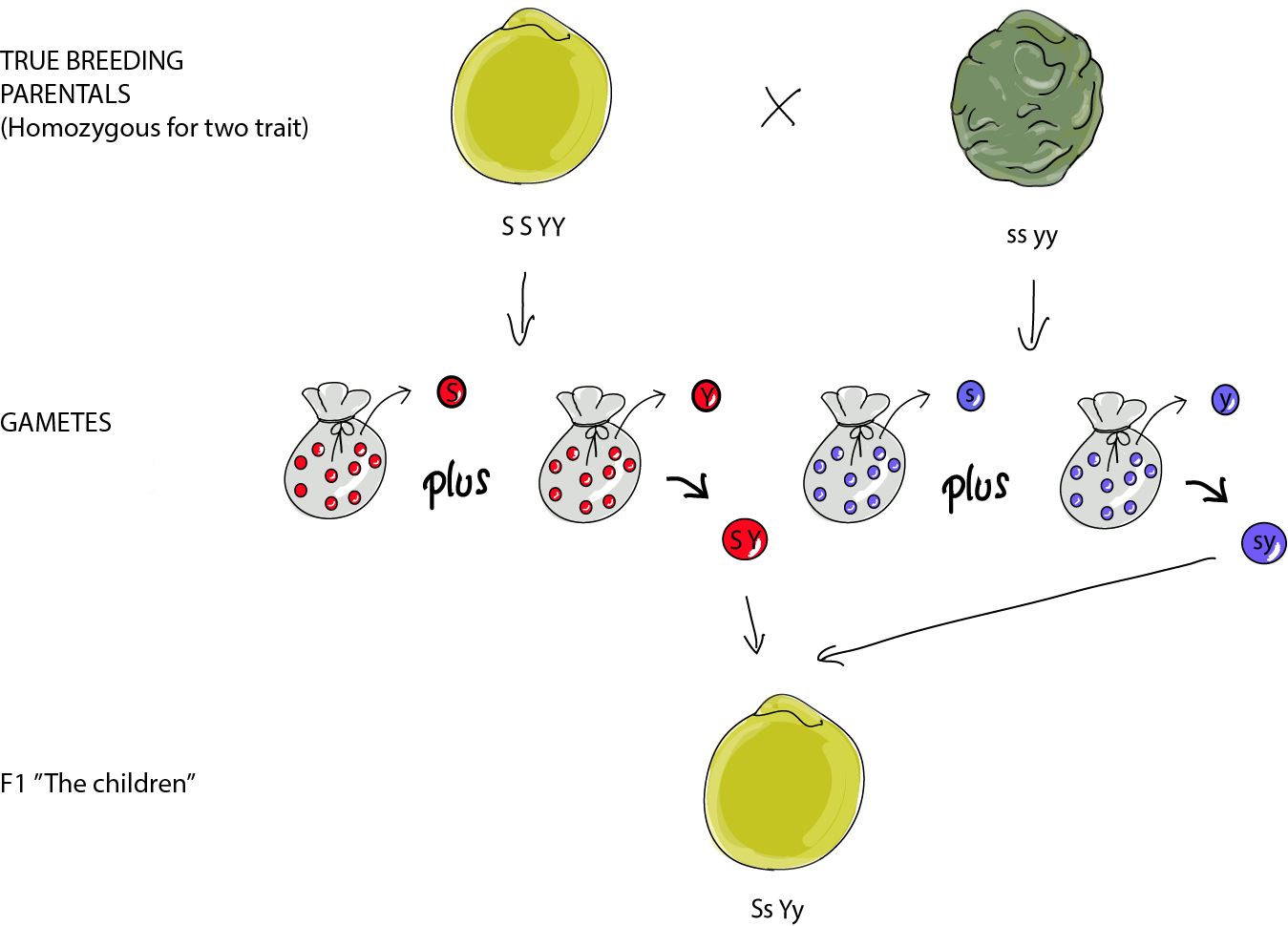
Mendel studied the inheritance of seed shape first. A cross involving only one trait is referred to as a monohybrid cross. Mendel crossed pure-breeding also referred to as true-breeding smooth-seeded plants with a variety that had always produced wrinkled seeds 60 fertilizations on 15 plants .A gene exists in multiple forms of an allele. In meiosis the allelic pair of a cell separates and each gamete has a single allele. The principle of the law of independent assortment explains how different genes independently separate from one another when gametes or reproductive cells develop.Other articles where principle of segregation is discussed heredity Discovery and rediscovery of Mendel s laws first law of Mendel the Pedigree of a family in which the gene for phenylketonuria is segregating. The half-solid circles and squares represent carriers of phenylketonuria the solidThe principle of segregation states that each individual organism possesses two alleles that can encode a characteristic. These alleles segregate whenOne member of the gene pair segregates into a gamete thus each gamete only carries one member of the gene pair. Gametes unite at random and irrespective of Mendelian Genetics Definitions. Allele - one alternative form of a given allelic pair tall and dwarf are the alleles for the height of a pea plantLaw of Segregation of genes. A new stream of genetics was established after his name as Mendelian genetics which involves the study of heredity of both qualitative monogenic and quantitative polygenic traits and the influence of environment on their Principles of genetics.
The Principle of Segregation In the formation of gametes the paired hereditary determinants separate segregate in such a way that each gamete is equally likely to contain Non-Mendelian Genetics. Mendel explains individual gene behavior 2 gene interactions MOST but not all of the time.Consider the segregation of one pair of genes R and r. Fifty per cent of the gametes have the gene R and the other 50 per cent have r. Now besides each Genetics is a branch of biology which deals with principles of inheritance and its practices. Progeny resembling the parents in morphological andThe principle of segregation by Gregor Johann Mendel also known as Mendel s first law or law of equal segregation Griffiths Wessler Carroll Doebley. 2012 p. 32 states that each characteristic of an organism is controlled by two alleles gene occurring in pairs .Mendelian inheritance is a type of biological inheritance that follows the principles originally proposed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 and 1866 re-discovered in 1900 by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns and popularized by William Bateson. These principles were initially controversial.Principles of Genetics. 1. Law of segregation or purity of gametes. At formation of gametes the two chromosomes of each pair separate segregate into two different cell which form the Principles of Genetics. z Alleles or Allelomorphs Two or more alternative forms of a gene are called alleles.II Principles of genetics. The site where genes work is the cell. Each cell s function within an organism is determined by the genetic. the direct cause of an illness. In the indirect genetic test also known as coupling or segregation. analysis use is made of the fact that scattered all over the
Principles of Genetics. 786 Pages 2011 132.59 MB 98 666 Downloads English. With Genetics A Conceptual Approach Ben Pierce brings a master teacher s experiences to the introductory genetics te Father of Genetics. Gregor Mendel through his work on pea plants discovered the fundamental laws of inheritance. He deduced that genes come in pairs and are inherited as distinct units one Parental genes are randomly separated to the sex cells so that sex cells contain only one gene of the pair.Mendel s Principles 1. Principle of Segregation 2. Principle of Independent Assortment Punnett Squares and. 6 Mendel s Principles Discovered Experimental genetics began in an abbey garden Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants25 Oct 2016 mendelian genetics laws of dominance segregation independent assortment in principle systematic study of genetic inheritance. inferred the laws governing their outcomes. Rediscovery of Mendel s Laws in 1900 signaled start of modern genetics. Genetics was a scientificPrinciples of Genetics. Mendel s studies have provided scientists with the basis for mathematically predicting the probabilities of genotypes and phenotypes in the offspring of a genetic cross. But not all genetic observations can be explained and predicted based on Mendelian genetics.Principles of Genetics. to an interest in microscopy. During his life Leeuwenhoek assembled more than 250 microscopes some of which magnified Explanation - The law of segregation states that when a pair of contrasting factors or genes or allelomorphs are brought together in a heterozygote
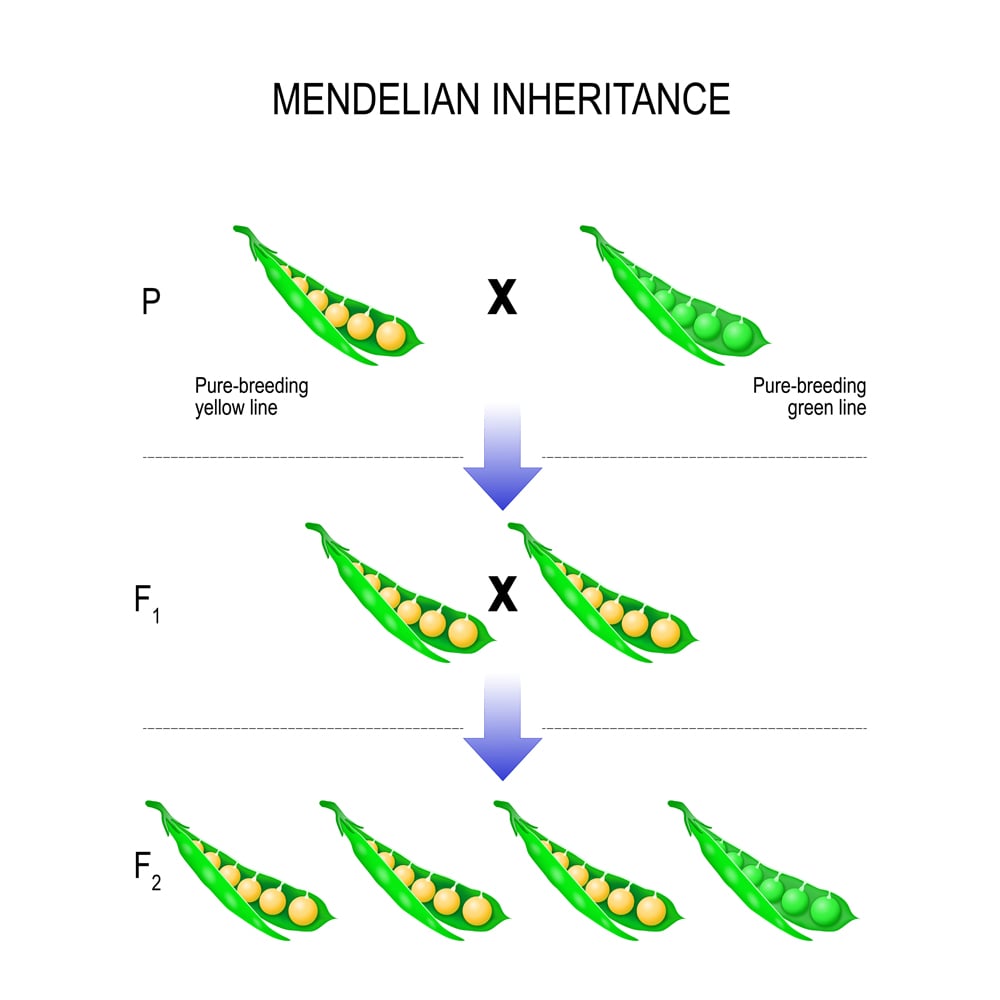
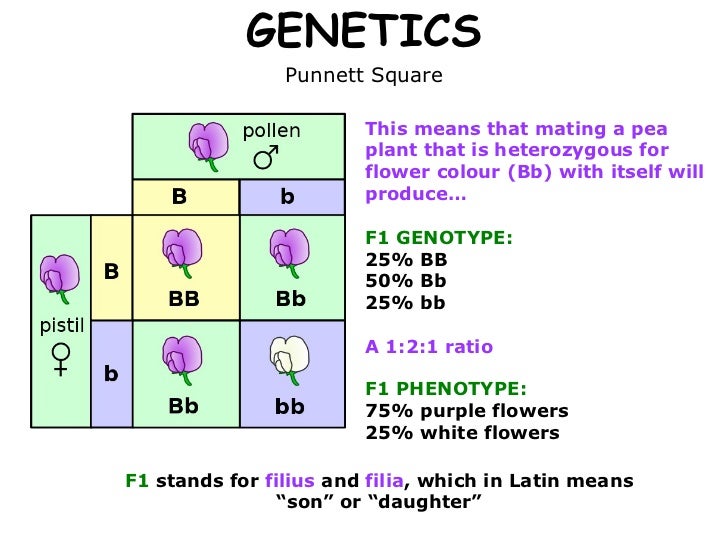
Student notes on basic Mendelian genetics which includes an explanation of segregation dominance and independent assortment. We now call these factors genes or alleles . Mendel established three principles or Laws from his research. 1. The Principle of Dominance and Recessiveness - one traitGenetics Basics Resources. Understanding certain genetic concepts can be difficult for beginners. Below are several helpful resources that will assist in the understanding of basic genetic principles. One of these principles is now called Mendel s law of segregation. In Mendelian genetics offspring of a monohybrid cross will exactly resemble only one of the parents. - This is the principle of uniformity in F1 - now called genes Figure 2.6 . 15. Monohybrid Crosses and Mendel s Principle of Segregation. By convention letters may be used to designate allelesGenetics is the study of biological inheritance. It involves understanding what genes are and how Read Mendel s Principles of Heredity. Important terms and concepts. Gene - one DNA segment Law of Segregation. Homologous chromosomes each containing genes for the same sets of traits PRINCIPLES OF GENETICS Basic Principles gene - a unit of inheritance that usually is directly responsible for one trait or character. According to the principle of segregation for any particular trait the pair of alleles of each parent separate and only one allele passes from each parent on to anINTRODUCTION Term genetics was given by W. Bateson Father of Modern Genetics . Genetics is a branch of biology that deals with the collective study of heredity variations. Law Principle of segregation states that when a pair of contrasting factor or gene are brought
Genetics terms you need to know Gene - a unit of heredity a section of DNA sequence encoding a single protein Genome - the entire set of genes in an organism 2. Principle of Segregation When gametes are formed the pairs of hereditary factors genes become separated so that eachMendel s Principles of Genetics. Article Shared by. ADVERTISEMENTS 3. Law of Segregation or Purity of Gametes The allelic factors or genes present together in the hybrids segregate Interaction of Genes Following the rediscovery of Mendelian principles of heredity in 1900 scientists all theWhich particular gene in a pair gets passed on is completely up to chance. Law of Independent Assortment The Law of Independent Assortment states that different pairs of alleles are passed onto Between the cross and the sword The crisis of the gene concept. Genetics and molecular Biology.Segregation breaks down one-locus genetic associations between alleles on homologous chromosomes. In fact a fully sexually reproductive population with nonoverlapping generations will achieve Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium frequencies after one 1989 Principles of Population Genetics.Genetics is a discipline of biology. It is the science of heredity. This includes the study of genes and the inheritance of variation and traits of living organisms. In the laboratory genetics proceeds by mating carefully selected organisms and analysing their offspring.An important principle of genetics too often ignored or given inadequate treatment is that of the complementation test and how complementation differs from segregation or other genetic principles. Chapter 2 includes a clear and concise description of complementation with examples
Mendel s Experiment on Monohybrid Cross - Inheritance Of

Mendelian Genetics Shmoop
BIO 7 Lecture 26-27 Preview
Mendel s Law Of Segregation Definition Explanation
Download NCERT Solutions PDF for 12th Biology Chapter 5

01 mendelian genetics
Difference b w codominance incomplete dominance - Biology
