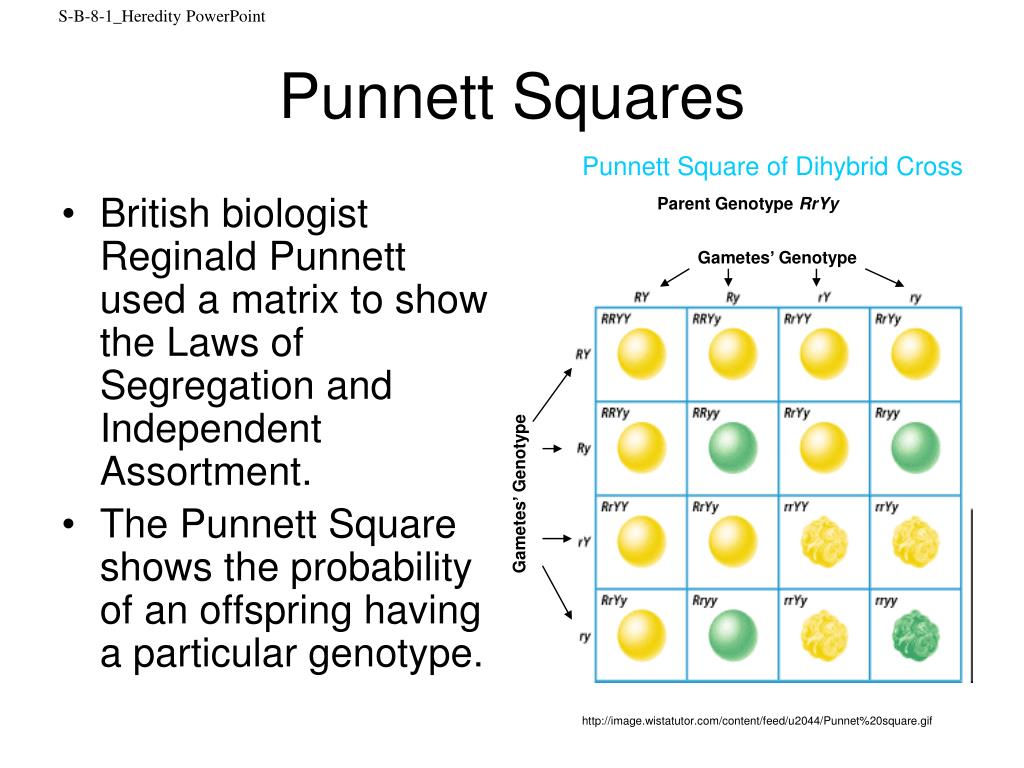
F1 Punnett Square
Solved Draw The F1 Punnett Square . Label The Diagram By D
Solved Draw the F1 Punnett square. Label the diagram by Chegg.com. Draw the F1 Punnett square. Label the diagram by dragging the labels to the appropriate targets. Predict the expected F 1 phenotype s . yellow seeds and inflated pods green seeds and inflated pods yellow seeds and constricted pods green seeds and constricted pods.By looking at the Punnett square we see that there are three possible genotypes that could result from this crossing AA Aa aa. The genotypes AA and Aa will result in the yellow pea phenotype because A is dominant. Only aa will produce the green pea phenotype. Now we see how it was possible for the green pea phenotype to skip a generation.The Punnett square calculator provides you with an answer to that and many other questions. It comes as handy if you want to calculate the genotypic ratio the phenotypic ratio or if you re looking for a simple ready-to-go dominant and recessive traits chart. Moreover our Punnet square maker allows you to calculate the probability that a Punnett square is a grid formed by 4 squares to form a larger square. Scientists use this as a way to predict a trait or genotype that comes from two different people or organisms. Before talking about how to use a Punnett square the next important topic is alleles and the different types of alleles. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the body.Punnett Square Definition A Punnett square is a graphical representation of the possible genotypes of an offspring arising from a particular cross or breeding event. Creating a Punnett square requires knowledge of the genetic composition of the parents. The various possible combinations of their gametes are encapsulated in a tabular format.
This Punnett square represents a cross between two pea plants that are heterozygous for two characteristics. G represents the dominant allele for green pod color and g represents the recessive allele for yellow pod color. F represents the dominant allele for full pod form and f represents the recessive allele for constricted pod form. SummaryMaking a Punnett Square 1 Draw a 2 x 2 square. Draw a box and divide it into four smaller squares. Leave room above the box and to its left so you can label it. Review the background information below if you have trouble understanding any of the steps that follow. 2 Name the alleles involved.To draw a square write all possible allele combinations one parent can contribute to its gametes across the top of a box and all possible allele combinations from the other parent down the left side. The allele combinations along the top and sides become labels for rows and columns within the square.PUNNETT SQUARE CHEAT SHEET Below is a sampling of Punnett Square problems that you will be expected to solve. In order to do this you will also have to understand the meaning of the terms below. Genotype The letters that make up the individual. E.g. TT or Tt Phenotype The physical characteristics of the particular trait. E.g. Tall or shortThe Punnett square is a diagram that is used to predict an outcome of a particular cross or breeding experiment. It is named after Reginald C. Punnett who devised the approach to determine the probability of an offspring s having a particular genotype combination of alleles .
Punnett squares are diagrams designed to predict results of classic breeding experiments. They support Mendelian inheritance as well as the laws of segregation and independent assortment. During meiosis chromatids are separated such that each gamete receives only one allele.We determine the entry in each cell in the Punnett square by looking at the alleles in the row and column of that entry. In what follows we will construct Punnett squares for all possible situations of a single trait. Two Homozygous Parents If both parents are homozygous then all of the offspring will have an identical genotype.The yellow-pod parent gg will prcduce g gametes. Step 4 Enter the possible gametes at the top and side of the Punnett square. At this point the Punnett square for this problem would look like this Step 5 Complete the Punnett square by writing the alleles from the gametes in the appropriate boxes.A Punnett Square so named after it s creator Reginald C. Punnett is a chart drawn to determine the probable results of a genetic cross. It will show you every possible combination of offspring that result from a cross. Therefore a Punnett square is a prediction that estimates what we should see in nature. How does a Punnett Square Work Follow this method to construct Punnett squares. Determine the parental genotypes - the allele combinations for the male and female. You can use any letter you like but select one that has a
So the math would go 1 2 1 2 1 4 chance your child will have blue eyes The first 1 2 is the probability that your mother gave YOU a little b the second 1 2 is the probability that you would give that little b on if you had it. Sorry it s so long hope it helped 5 comments 159 votes See 5 more replies Hans 9 years agoHow to construct Punnett squares Determine the parental genotypes. You can use any letter you like but select one that has a clearly different lower case for example Aa Bb Dd. Split the allelesDraw a 2 x 2 grid. As its name suggests a Punnett square is just a divided square. Draw your square and divide it into four smaller squares by drawing two lines one horizontal and one vertical through the center of the square. Leave enough room in each box for two letters. Also leave room at the top and left side of the square. 3tion of the chromosomes d formation of the nuclear membrane e attachment of microtubules to the kineto - chores and f migration of centrosomes to positions on opposite sides of the nucleus. ANS c f a e b d . 2.11 In human beings the gene for b-globin is located on chro-mosome 11 and the gene for a-globin which is The Punnett square shows the possible allele combinations that result from a two-factor cross between pea plants. Both pea plants are heterozygous for seed shape round R and wrinkled r and pod color green Y and yellow y . Which of the following conclusions can be reached about the offspring of this cross
The Punnett square below makes it clear that at each birth there will be a 25 chance of you having a normal homozygous AA child a 50 chance of a healthy heterozygous Aa carrier child like you and your mate and a 25 chance of a homozygous recessive aa child who probably will eventually die from this condition.allele. Start by indicating the genotypes of E and F. Then use the Punnett Square to figure out what the genotypes for C and D must be. Next determine the genotypes of A and B. Finally determine the genotype of G. Many other genes are inherited in the same manner as this recessive allele which causes albinism.These type of crosses can be challenging to set up and the square you create will be 4x4. This simple guide will walk you through the steps of solving a typical dihybrid cross common in genetics. The method can also work for any cross that involves two traits. Consider this cross.Therefore we use a 4 square by 4 square Punnett Square. Alleles from both parents Now we can predict the outcome of the genetic cross of AaBb x AaBb. To determine the fraction of the offspring homozygous for both traits first determine the genotype of an offspring homozygous for both traits. It would be aabb. Label your answer with the proper units. d What is the genetic distance between the bl and st loci Label your answer with the proper units. e Draw a genetic map showing the correct order of the hb bl and st loci. 2. The following mouse pedigree shows the segregation of two different mutant traits.
A Punnett square to use for this problem is shown in the following figure. See page 291 of your text for the labeled figure. If a carrier mates with a male who has normal color vision there is a 50 chance that each daughter will be a carrier like her mother and a 50 chance that each son will have the disorder.In the following diagram 3 pairs of Rh alleles C c D d E e occur at 3 different loci on homologous chromosome pair 1. Punnett square . When you determine the fractional probability of a taster type B child multiply by 1 2 to include the sex of the child. Questions 91 - 94. Another way to solve this problem is to multiply 1 Punnett Squares To determine the inheritance of red-green colorblindness or any other X-linked trait the genotypes of the parents must be considered.For example if a mother is a carrier for colorblindness X X c and a father has normal vision X Y then their sons have a 50 chance of colorblindness because they inherit their X All problems are to be completed on a separate sheet of paper. Be sure to label each heading. Answer each question and show work Punnett squares fully. Example Problems Monohybrid 1. An allele for brown eyes B is dominant over that for blue eyes b. A blue-eyed man both of whose parents were brown-eyed marries a brown-eyed woman.
F1 In Punnett Square - Mendelian Genetics Punnett square

EXPERIMENT 1 PUNNETT SQUARE CROSSES Part 1 Post-Lab

8. Punnett Squares HSC biology - YouTube

Demystifying Genetic Drift Answers in Genesis

What Is A Punnett Square And Why Is It Useful In Genetics

PPT - Bellringer Complete the Punnett Square PowerPoint

Corn Lab - Alyssa s Site
Mendel s law of Independent Assortment - Study Solutions
Finley Period 4 Tuesday April 5th

PPT - Heredity PowerPoint Presentation free download - ID
Aabb x aabb. Dihybrid Crosses Quiz. 2019-01-21
Designer Genes - Science Olympiad Student Center Wiki
PPT - Genetics PowerPoint Presentation - ID 3596375
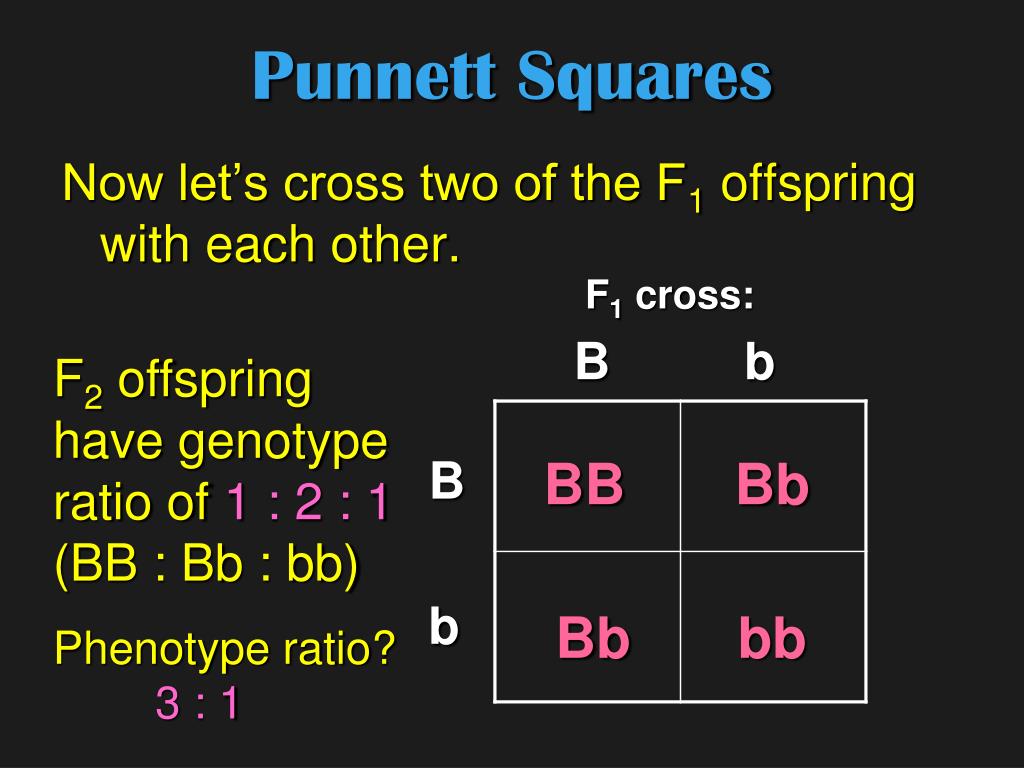
Punnett squares

Solved Complete The Following Punnett Squares In Your Lab

This Punnett square shows how two pea plants with Chegg.com
Biology Final 2010 48 Punnett Square
